Tistory View
단순 드라이브 목록
단순히 드라이브목록만 구하려면 다음과 같이 할 수 있다.
방법1 - GetLogicalDrives
List1 - 루트목록1
void DiplayDrives1()
{
DWORD drives = GetLogicalDrives();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if ( drives & ( 1 << i ) ) {
wprintf(L"%c\n", L'A' + i );
}
}
}bit의 위치가 SET되으면 그 드라이브가 존재한다는 뜻이다.
만약 5번째 비트가 SET되어 있다면, ABCD(E)F.. 중 E드라이브가 있다는 뜻이 된다. 대부분의 상황에서 이 방법은 잘 작동한다. 사용법은 단순하지만, 이 방법은 26번의 루프를 돌아야 될 뿐만 아니라, 드라이브명은 재가공이 필요하다.
방법2 - GetLogicalDriveString
List2 - 루트목록2
void DiplayDrives2()
{
DWORD rcc;
wchar_t * bufPtr = NULL;
DWORD bufLen = 0;
wchar_t* p;
// rcc required size
bufLen = GetLogicalDriveStringsW( 0, NULL );
//wprintf(L"rcc=%d", rcc);
if (bufLen <= 0 ) {
wprintf( L"Something goes wrong!\n");
return;
}
bufPtr = (wchar_t*)malloc( (bufLen + 1 ) * sizeof( wchar_t ) );
if (!bufPtr ) {
wprintf(L"out of memory\n");
return;
}
rcc = GetLogicalDriveStringsW( bufLen, bufPtr );
p = bufPtr;
while ( *p ) {
UINT type = GetDriveTypeW(p);
wprintf( L"drive %s %s\n", p, GetDriveTypeText( type ) );
p += wcslen( p ) + 1;
}
if ( bufPtr ) {
free( bufPtr );
}
}이 방법은 GetLogicalDrivString함수를 이용한다. 각각의 드라이브명이 NULL로 구분되고 마지막은 두개의 NULL로 구성된다.

출력을 보면 드라이브명에 역슬래쉬가 붙은 경로명으로 값을 구할 수 있다. 방법1과의 차이는 경로명으로 구할 수 있다는 점이다. 사실상 폴더명으로 뽑을 지 비트로 뽑을지의 차이뿐인 것 같다.
| GetDriveType함수는 USB스틱의 경우, DRIVE_REMOVABLE과 같이 제거가 가능하다고 대부분 뜨지만, 가끔식 DRIVE_FIXED로 뜨는 경우도 있다. 보통 아주 빠른 USB드라이브의 경우에 이렇게 된다. |
보통의 사용하는 루트로 마운트되는 모든 드라이브를 구하는 데에는 위의 두방법으로 충분하다. 하지만 위의 두 방법은 드라이브의 루트로 된 경우만을 뽑아 낼 수 있다. 윈도우에서도 파티션을 드라이브가 아닌 폴더로 붙여 사용할 수가 있다. (mklink를 사용하는 방법과 파티션 마운트자체를 폴더로 마운트하는 방법)
방법3 - FindFirstVolume, FindNextVolume, FindVolumeClose
List3 - 볼륨목록1
void DiplayDrives3()
{
HANDLE handle = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
const DWORD VOLUMENAME_SIZE = 512;
wchar_t szVolumeName[VOLUMENAME_SIZE];
handle = FindFirstVolumeW( szVolumeName, VOLUMENAME_SIZE );
while (handle != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
wprintf( L"drive %s\n", szVolumeName );
if (!FindNextVolumeW(handle, szVolumeName, VOLUMENAME_SIZE)) {
break;
}
}
if (handle != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE )
{
FindVolumeClose(handle);
}
}
함수이름에서도 알 수 있듯이 볼륨단위로 드라이브를 순회하면서 구할 수 있다.또한 이 방법은 마운트 되지 않는 볼륨도 뽑아 낸다. 이 볼륨이 어디에 링크 되어 있는지 알아야 하기에 다음의 방법으로 추가 작업을 해야 한다.
이 방법은 네트웍크 드라이브는 추출되지 않는다. 네트워크 드라이브는 방법1,2에서 따로 추출해야 한다.
List4 - 볼륨목록2
void DiplayDrives4()
{
HANDLE handle = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
const DWORD VOLUMENAME_SIZE = 512;
DWORD CharCount = 0;
DWORD Error;
WCHAR DeviceName[MAX_PATH] = L"";
wchar_t szVolumeName[VOLUMENAME_SIZE];
handle = FindFirstVolumeW(szVolumeName, VOLUMENAME_SIZE);
while (handle != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
//wprintf(L"drive %s\n", szVolumeName);
size_t Index = wcslen(szVolumeName) - 1;
if (szVolumeName[0] != L'\\' ||
szVolumeName[1] != L'\\' ||
szVolumeName[2] != L'?' ||
szVolumeName[3] != L'\\' ||
szVolumeName[Index] != L'\\')
{
//Error = ERROR_BAD_PATHNAME;
wprintf(L"FindFirstVolumeW/FindNextVolumeW returned a bad path: %s\n", szVolumeName );
break;
}
szVolumeName[Index] = L'\0';
CharCount = QueryDosDeviceW(&szVolumeName[4], DeviceName, ARRAYSIZE(DeviceName));
szVolumeName[Index] = L'\\';
if (CharCount == 0)
{
Error = GetLastError();
wprintf(L"QueryDosDeviceW failed with error code %d\n", Error);
break;
}
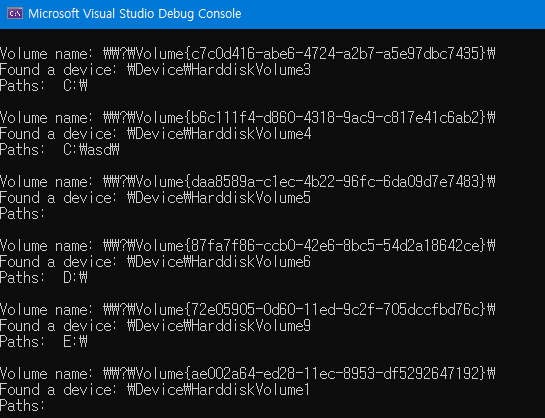
wprintf(L"\nVolume name: %s", szVolumeName);
wprintf(L"\nFound a device: %s", DeviceName);
wprintf(L"\nPaths:");
DisplayVolumePaths(szVolumeName);
if (!FindNextVolumeW(handle, szVolumeName, VOLUMENAME_SIZE)) {
break;
}
}
if (handle != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
FindVolumeClose(handle);
}
}
List5 - GetVolumePathNamesForVolumeName : Volume이름으로 Path구하기
void DisplayVolumePaths( PWCHAR VolumeName )
{
DWORD CharCount = MAX_PATH + 1;
PWCHAR Names = NULL;
PWCHAR NameIdx = NULL;
BOOL Success = FALSE;
for (;;)
{
//
// Allocate a buffer to hold the paths.
Names = (PWCHAR) new BYTE[CharCount * sizeof(WCHAR)];
if (!Names)
{
//
// If memory can't be allocated, return.
return;
}
//
// Obtain all of the paths
// for this volume.
Success = GetVolumePathNamesForVolumeNameW(
VolumeName, Names, CharCount, &CharCount
);
if (Success)
{
break;
}
if (GetLastError() != ERROR_MORE_DATA)
{
break;
}
//
// Try again with the
// new suggested size.
delete[] Names;
Names = NULL;
}
if (Success)
{
//
// Display the various paths.
for (NameIdx = Names;
NameIdx[0] != L'\0';
NameIdx += wcslen(NameIdx) + 1)
{
wprintf(L" %s", NameIdx);
}
wprintf(L"\n");
}
if (Names != NULL)
{
delete[] Names;
Names = NULL;
}
return;
}
GetVolumePathNameW 는 파일이나 폴더가 어떤 볼륨에 속해있는 지를 알게 해준다. 이 결과를 드라이브의 루트가 아닌 sub일수 있다. 아래의 출력에서 두번째 볼륨이 "C:\asd\"에 마운트되어 있다.
레퍼런스
이런 작업을 위해 관련 함수를 모아둔 링크는 다음과 같다.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/FileIO/volume-management-functions
Volume Management Functions - Win32 apps
Functions used in volume management.
docs.microsoft.com
----
'MS Windows' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 윈도우 11 동영상(음악)있는 폴더만 들어가면 느려지는... (0) | 2024.03.09 |
|---|---|
| WinSxS 폴더 크기 줄이기 (3) | 2023.09.30 |
| LDPlayer 개발자모드 (1) | 2022.07.29 |
| VC 드라이브 볼륨 시리얼번호등 정보 알아내기 (2) | 2022.07.27 |
| 윈도우 폴더를 드라이브로 subst (1) | 2022.07.25 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- Android
- texture
- 전기요금
- OpenGLes
- 컴퓨트쉐이더
- 에어컨
- 재태크
- TTS
- choreographer
- 예금
- 재테크
- 전기세
- 공유 컨텍스트
- 애드센스
- 아끼는 법
- gpgpu
- 사용료
- 전기료
- 경제보복
- 애드핏
- 컴퓨트셰이더
- OpenGL ES
- 티스토리
- 블로그
- 안드로이드
- 에어콘
- 적금
- 금리
- 텍스처
- ComputeShader
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |